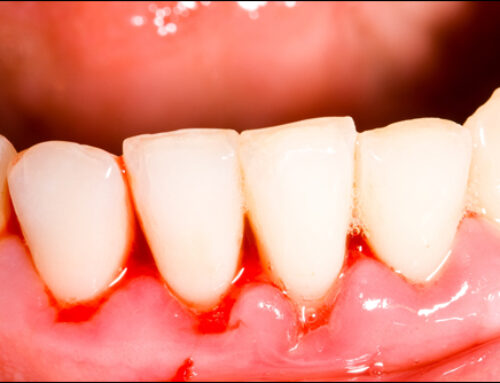
Gum pain can be a troubling and uncomfortable experience that affects your overall oral health and quality of life. Understanding the causes, effective treatments, and preventive measures can help alleviate discomfort and maintain a healthy smile.
Causes
-
- Gum Disease: One of the most common causes of gum pain is gum disease, including gingivitis and periodontitis. Gingivitis, the early stage of gum disease, is characterized by redness, swelling, and bleeding of the gums, often caused by plaque buildup. If untreated, it can progress to periodontitis, leading to deeper gum infection, bone loss, and more severe pain.
- Gum Recession: Gum recession occurs when the gum tissue pulls back from the teeth, exposing the tooth roots. This condition can result from aggressive brushing, periodontal disease, or genetic factors, leading to sensitivity and discomfort in the exposed areas.
- Infections: Gum infections, such as abscesses or oral thrush, can cause localized pain and swelling. An abscess is a pocket of pus caused by bacterial infection, while oral thrush is a fungal infection that can lead to sore, inflamed gums.
- Teething and Orthodontic Adjustments: In children, gum pain can be associated with teething as new teeth emerge. Similarly, orthodontic treatments, such as braces, can cause temporary gum discomfort due to adjustments and pressure on the teeth.
- Other Causes: Additional factors contributing to gum pain include trauma or injury to the gums, hormonal changes (such as during pregnancy), certain medications, and systemic conditions like diabetes.
 Treatments
Treatments
-
- Oral Hygiene Improvement: Maintaining excellent oral hygiene is crucial. Brush your teeth twice daily with a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste. Floss daily to remove plaque and food particles from between your teeth and under your gumline.
- Salt Water Rinses: Rinsing your mouth with a warm salt water solution can help reduce inflammation and soothe sore gums. Mix one teaspoon of salt in a cup of warm water and swish it around your mouth for about 30 seconds.
- Over-the-Counter Remedies: Non-prescription pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can help manage gum pain. Topical numbing gels may also provide temporary relief.
- Professional Dental Care: If gum pain persists, consult your dentist. They can diagnose the underlying cause and provide appropriate treatments, such as scaling and root planing for gum disease or medication for infections.
Prevention
-
- Regular Dental Check-Ups: Visit your dentist regularly for cleanings and examinations to catch and address potential issues early.
- Proper Brushing and Flossing: Use a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste, and floss daily to prevent plaque buildup and gum disease.
- Avoid Tobacco Products: Smoking and chewing tobacco can exacerbate gum problems and delay healing.
- Healthy Diet: Eat a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals to support gum health. Avoid sugary foods that can contribute to plaque buildup.
Addressing gum pain promptly and effectively is essential for maintaining oral health and comfort. By understanding the causes, utilizing appropriate treatments, and practicing preventive measures, you can manage and reduce pain, ensuring a healthier, more comfortable smile. If you experience persistent or severe pain, don’t hesitate to seek professional dental care for a comprehensive evaluation and treatment plan.