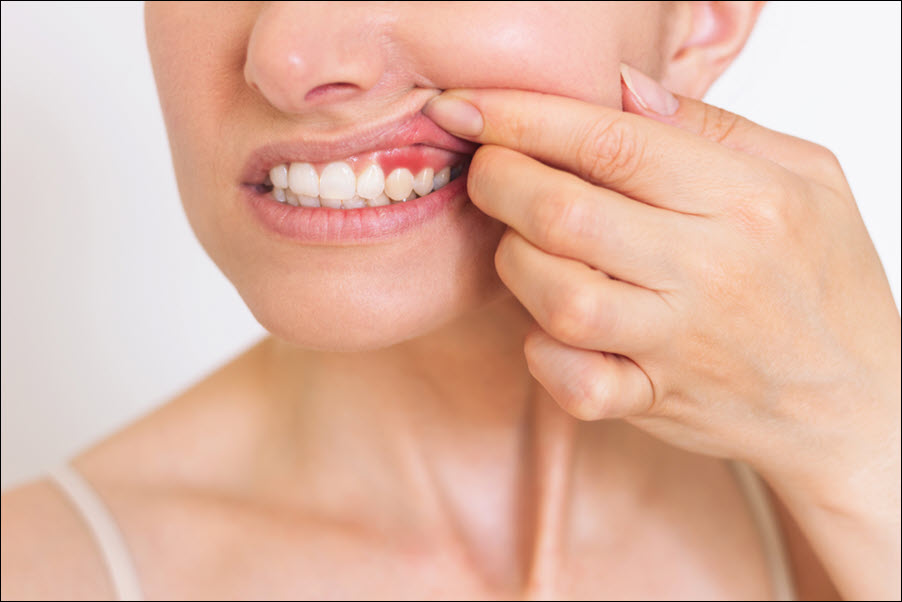
Periodontal disease damages the gums and supporting structures of the teeth. It begins with plaque buildup, leading to gum inflammation and infection. Without treatment, it progresses to periodontitis, causing gum recession, bone loss, and tooth damage. Early detection and treatment prevent serious complications and protect oral health. Proper brushing, flossing, and regular dental checkups reduce plaque and strengthen gum tissue. Correcting gum disease improves tooth stability and reduces inflammation. Understanding the signs and treatment options for periodontal disease ensures long-term oral health. Let’s explore how to recognize, prevent, and correct periodontal disease effectively.
Signs of Periodontal Disease
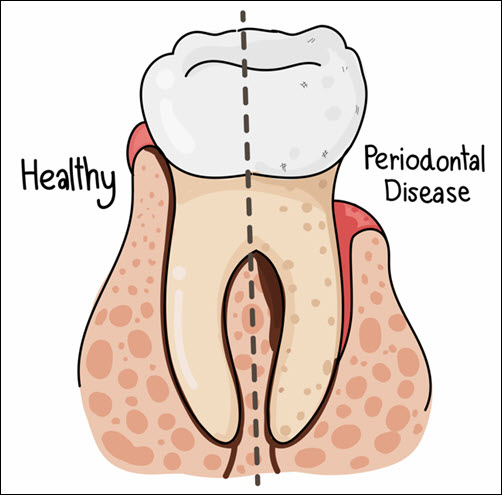 Bleeding gums while brushing or flossing signal early-stage gum disease (gingivitis). Red, swollen, and tender gums indicate inflammation and bacterial buildup. Persistent bad breath (halitosis) results from plaque and gum infection. Receding gums expose tooth roots, increasing sensitivity and the risk of decay. Loose teeth or changes in bite alignment reflect bone loss and weakened tooth support. Pus between the teeth and gums signals advanced infection. Gum pockets deeper than 3 mm indicate periodontitis. Early detection prevents further damage and improves treatment success. Regular dental exams identify gum disease signs early. Treating symptoms early reduces complications and improves gum health.
Bleeding gums while brushing or flossing signal early-stage gum disease (gingivitis). Red, swollen, and tender gums indicate inflammation and bacterial buildup. Persistent bad breath (halitosis) results from plaque and gum infection. Receding gums expose tooth roots, increasing sensitivity and the risk of decay. Loose teeth or changes in bite alignment reflect bone loss and weakened tooth support. Pus between the teeth and gums signals advanced infection. Gum pockets deeper than 3 mm indicate periodontitis. Early detection prevents further damage and improves treatment success. Regular dental exams identify gum disease signs early. Treating symptoms early reduces complications and improves gum health.
How to Prevent Periodontal Disease
Brushing and flossing daily prevent plaque buildup and gum inflammation. Brush twice a day with a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste. Floss daily to remove food particles and plaque between teeth. Use an antibacterial mouthwash to kill bacteria and freshen breath. Drink water throughout the day to improve saliva flow and wash away debris. Avoid smoking and tobacco use, which weaken gums and slow healing. Eat a balanced diet rich in vitamins C and D to strengthen gum tissue and bone health. Schedule regular dental cleanings every six months to remove plaque and tartar. Preventing gum disease ensures stronger, healthier teeth and gums.
Professional Dental Cleanings and Deep Scaling
Professional dental cleanings remove plaque and tartar that brushing and flossing miss. Dentists use ultrasonic tools to clean below the gumline and reduce inflammation. Scaling removes hardened tartar from the tooth surface and gum pockets. Root planing smooths the tooth root, encouraging gum reattachment and reducing pocket depth. Local anesthetics improve comfort during deep cleaning procedures. Improved gum attachment reduces sensitivity and strengthens tooth support. Dentists recommend scaling and root planing for mild to moderate gum disease. Regular cleanings prevent plaque buildup and improve gum health. Professional care reduces inflammation and prevents further gum recession.
Surgical Correction for Severe Periodontal Disease
Advanced periodontitis often requires surgical treatment. Flap surgery lifts the gum tissue to remove deep plaque and tartar. Soft tissue grafting covers exposed roots and restores gum tissue. Bone grafting rebuilds lost bone and strengthens tooth support. Guided tissue regeneration promotes new bone and tissue growth. Pocket reduction surgery decreases gum pocket depth and improves gum attachment. Oral antibiotics reduce bacterial infection and support healing. Surgery improves gum health, reduces tooth sensitivity, and restores tooth stability. Proper post-surgical care ensures faster healing and better gum strength. Surgical correction increases long-term gum health and tooth preservation.
How to Maintain Healthy Gums After Treatment
Maintaining good oral hygiene prevents gum disease from returning. Brush and floss daily to keep gums and teeth clean. Use an antibacterial mouthwash to reduce bacteria and plaque. Schedule professional cleanings every six months to monitor gum health and remove plaque buildup. Wear a night guard if you grind your teeth to reduce gum strain. Avoid smoking and sugary foods, which increase bacterial growth. Stay hydrated to improve saliva flow and protect gum tissue. Early treatment of gum inflammation prevents disease progression. Consistent oral care strengthens gum tissue and reduces infection risk. Healthy gums improve tooth stability and overall oral health.
Periodontal disease begins with plaque buildup and gum inflammation. Bleeding, swelling, and bad breath signal early-stage gum disease. Loose teeth and gum recession reflect advanced periodontitis and bone loss. Brushing, flossing, and regular cleanings prevent plaque buildup and reduce inflammation. Professional scaling and root planing restore gum attachment and strengthen tooth support. Surgical correction repairs damaged tissue and improves gum health. Maintaining proper oral hygiene and regular dental checkups prevent future gum disease. Early detection and treatment protect tooth stability and improve overall gum health. Investing in gum care ensures a healthier smile and stronger teeth.


